lagdo / dbadmin-app
A web based database management tool with multiple DBMS support.
Installs: 2
Dependents: 0
Suggesters: 0
Security: 0
Stars: 0
Watchers: 0
Forks: 0
Open Issues: 0
Language:CSS
Type:project
pkg:composer/lagdo/dbadmin-app
Requires
- php: ^8.2
- jaxon-php/jaxon-laravel: ^5.0
- jaxon-php/jaxon-upload: ^2.1
- lagdo/dbadmin-driver-mysql: 0.21.*
- lagdo/dbadmin-driver-pgsql: 0.21.*
- lagdo/dbadmin-driver-sqlite: 0.21.*
- lagdo/jaxon-dbadmin: 0.26.*
- lagdo/laravel-facades: ^1.0
- lagdo/ui-builder-bootstrap5: 0.5.*
- laravel/fortify: ^1.28
- laravel/framework: ^12.0
- laravel/tinker: ^2.10.1
Requires (Dev)
- fakerphp/faker: ^1.23
- laravel/pail: ^1.2.2
- laravel/pint: ^1.13
- laravel/sail: ^1.41
- mockery/mockery: ^1.6
- nunomaduro/collision: ^8.6
- phpunit/phpunit: ^11.5.3
README
Jaxon DbAdmin is a database admin dashboard with multiple DBMS support, and a custom and extensible authentication system.
Features • Installation • Docker • Authentication • Configuration • Query audit • Data export • Data import
About Jaxon DbAdmin
Jaxon DbAdmin is built with Jaxon, Laravel and Bootstrap 5.
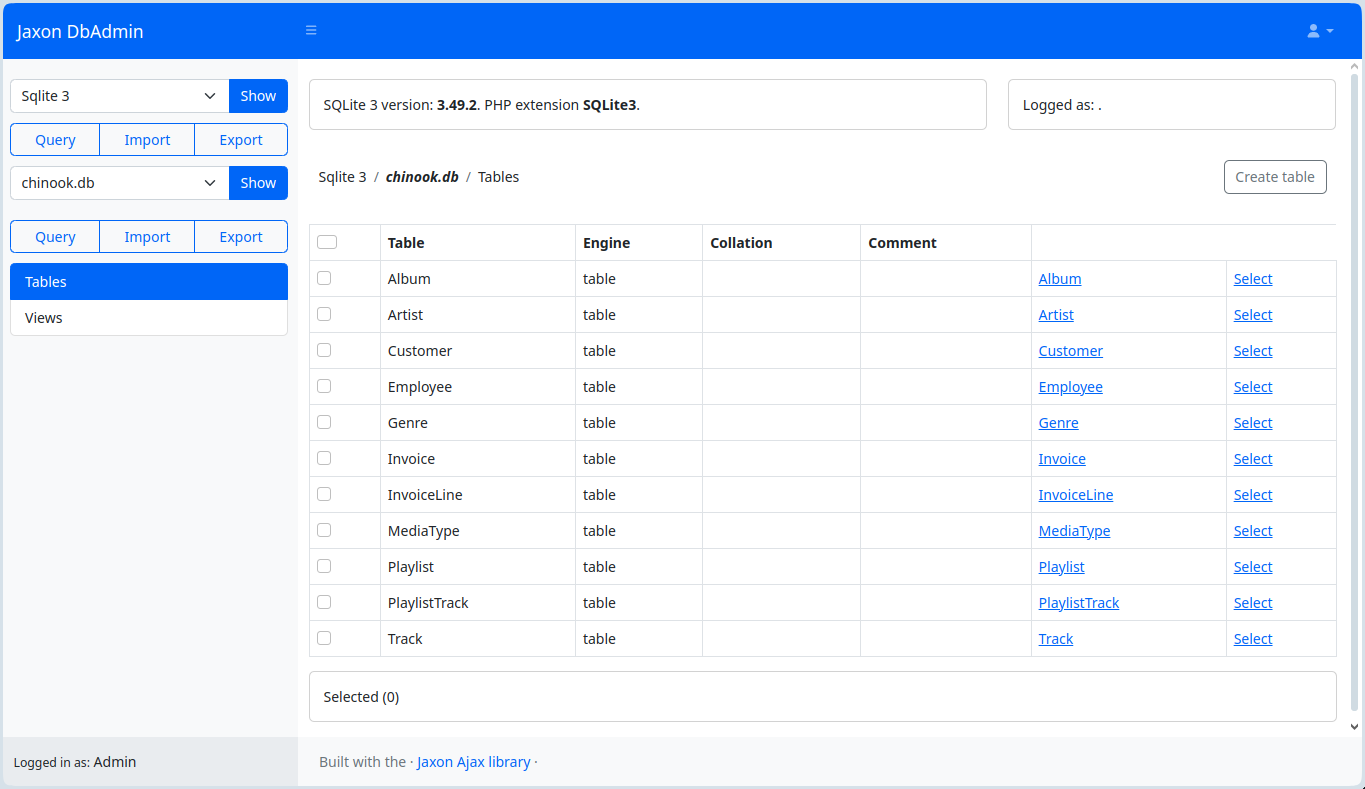
It currently supports 3 database servers: PostgreSQL, MySQL (and MariaDB), and SQLite.
Unlike other database management tools, Jaxon DbAdmin uses the Laravel authentication system instead of the database servers credentials to authenticate the application users.
The database access code (and thus the provided features) originates from Adminer. The original code was refactored to take advantage of the latest PHP features (namespaces, interfaces, DI, and so on), and separated into multiple Composer packages.
Here's the monorepo where the packages are developed: https://github.com/lagdo/dbadmin-mono.
Features and current status
This application and the related packages are still being actively developed, and the provided features are still basic and need improvements.
The following features are currently available:
- Browse servers and databases.
- Show tables and views details.
- Query a table.
- Query a view.
- Execute queries in the query editor.
- Use a better editor for SQL queries.
- Save and show the query history.
- Save queries in user favorites.
- Import or export data.
- Insert, modify or delete data in a table.
- Create or alter a table or view.
The following features are either disabled or not yet implemented, and planned for future releases:
- Drop a table or view.
- Navigate through related tables.
- Code completion for table and field names in the SQL editor.
- An advanced GUI-based query builder.
Installation
As a Laravel and PHP application, Jaxon DbAdmin needs to be installed with Composer.
Install from Packagist.
composer create-project lagdo/dbadmin-app dbadmin
Install from Github.
git clone https://github.com/lagdo/dbadmin-app dbadmin
cd dbadmin
composer install
composer run post-root-package-install
composer run post-create-project-cmd
By default, Jaxon DbAdmin stores the user credentials in a database. A SQLite database located at database/database.sqlite will be created and migrated during the installation.
A different database can be used. In this case, the .env and config/database.php file must be updated accordingly. See the Laravel database documention for more information.
The last step is to configure a web server to give access to the application directory, with the public subdir as index.
The database servers to be managed are listed in a config file, whose location and content are described in the Database access configuration section below.
Running with Docker
The Jaxon DbAdmin application can also be started with Docker.
docker run --rm --publish 8080:8080 --volume ./config/dbadmin.json:/var/www/config/dbadmin.json lagdo/jaxon-dbadmin:latest
or
docker run --rm -p 8080:8080 -v ./config/dbadmin.json:/var/www/config/dbadmin.json lagdo/jaxon-dbadmin:latest
In a docker-compose.yml file.
dbadmin: container_name: dbadmin image: lagdo/jaxon-dbadmin:latest volumes: - ./config/dbadmin.json:/var/www/config/dbadmin.json ports: - 8080:8080
The content of the config/dbadmin.json config file is described in the Database access configuration section below.
User management and authentication
Unlike other database management tools, Jaxon DbAdmin does not use the database server credentials to authenticate the application users.
The user authentication is a separate process, which in this case is provided by the Laravel framework.
By default, the user accounts and credentials are stored in the application database (different from the managed databases), and by default a fresh Laravel installation will create and migrate an SQLite database located in the database/database.sqlite file.
The application database can be changed in the Laravel database configuration.
Jaxon DbAdmin provides a CLI command to create user accounts in its database. It is executed from the application install dir.
php artisan user:create --name <user name> --email <user email>
If the --name and --email are not provided, the CLI command will ask for them.
It will then ask to provide and confirm the user password, and if all the inputs are valid, the user account will be created.
Thanks to Laravel, more advanced authentication systems can be implemented quite easily. For example, Jaxon DbAdmin can be setup to authenticate its users on a company SSO service.
Database access configuration
Jaxon DbAdmin supports 3 file formats for its database access configuration options: json, yaml and php.
It will successively look for the config/dbadmin.json, config/dbadmin.yaml, config/dbadmin.yml and config/dbadmin.php, and loads the first it will find.
It will then parse the content of the config file, and return the options specific to the authenticated user.
This is an example of a json config file.
{
"common": {
"access": {
"server": false,
"system": false
},
"servers": {
"db-postgresql": {
"driver": "pgsql",
"name": "PostgreSQL 14",
"host": "env(DBA_PGSQL_HOST)",
"port": "env(DBA_PGSQL_PORT)"
},
"db-mariadb": {
"driver": "mysql",
"name": "MariaDB 10",
"host": "env(DBA_MARIA_HOST)",
"port": "env(DBA_MARIA_PORT)"
},
"db-mysql": {
"driver": "mysql",
"name": "MySQL 8",
"host": "env(DBA_MYSQL_HOST)",
"port": "env(DBA_MYSQL_PORT)"
}
}
},
"fallback": {},
"users": [{
"id": {
"users": [
"user1@company.com",
"user2@company.com"
]
},
"servers": {
"db-postgresql": {
"username": "env(DBA_PGSQL_USERNAME)",
"password": "env(DBA_PGSQL_PASSWORD)"
},
"db-mysql": {
"username": "env(DBA_MYSQL_USERNAME)",
"password": "env(DBA_MYSQL_PASSWORD)"
},
"laravel": {
"driver": "sqlite",
"name": "Laravel",
"directory": "env(SQLITE_LARAVEL_DIR)"
}
}
}, {
"id": {
"user": "admin@company.com"
},
"access": {
"server": true,
"system": true
},
"servers": {
"db-mariadb": {
"username": "env(DBA_MARIA_USERNAME)",
"password": "env(DBA_MARIA_PASSWORD)"
},
"db-mysql": {
"username": "env(DBA_MYSQL_USERNAME)",
"password": "env(DBA_MYSQL_PASSWORD)"
},
"sqlite-3": {
"driver": "sqlite",
"name": "Sqlite 3",
"directory": "env(SQLITE_DEFAULT_DIR)"
}
}
}]
}
The Jaxon DbAdmin config file can contain 3 sections, all of which are optional.
The common section
This section contains options that are shared for all users. The options in this section will be merged with the user options found. Which also means that if no entry is found for the user, these options are not returned.
The fallback section
The options in this section will be returned if no specific entry exists for the authenticated user in the users section.
These options will be merged with the common options.
The users section
This section must contain an array of options, each for a given user or group of users.
Each entry in the array must have an attribute with id key, which itself is an object with 4 possible attributes to identify the corresponding users:
user: a single user email.users: an array of user emails.role: a single user role.roles: an array of user roles.
The other attributes are the database options, described in the following paragraph.
If any entry is found here for the current user, its value will be merged with the common options.
The database options
The common, fallback and each entry in users array contain the same options, excepted the id option in the servers array items.
The servers option
The servers option lists the database servers to be managed.
For each entry, the key is the unique identifier used in requests to the Jaxon DbAdmin application.
The driver option indicate the corresponding DBMS: pgsql for PostgreSQL, mysql for MySQL or MariaDB, and sqlite for SQLite.
The name option is the name to be displayed in the application UI.
The other options depend on the DBMS.
For SQLite, the directory option is a directory where to look for database files.
Each file in the directory with the db, sdb or sqlite extension is listed as a database.
For the other DBMS, the host, port, username and password options will be used to connect to the database server. Only the port option optional.
Except for driver and name, the values for all the other options can be loaded from env vars.
In this case, the option need to be set in a specific format like env(DBA_PGSQL_HOST), where the value in the parenthesis is the env var name.
In addition to the default .env, the application also loads the .env.dbadmin file, which can be used to define the Jaxon DbAdmin specific env vars.
After the merge with the options in the common section, the entries in the servers options are filtered on valid values.
As a consequence, only the entries for which all the required options (except port) are provided will be returned in the final list.
The default option
The default option defines a server the application will connect to when the web page is loaded or refreshed.
The access option
The access option is an object that contains multiple options to define to which databases and to which part of the application the user will have access.
The access option can be defined at top level, in this case it applies to all the database servers, or it can be defined in a specific server options, to be applied only to that server.
In the access object, the system option defines if the user has access to system databases and schemas. If set to false, which is the default, the system databases will not be listed in the user account.
The server option defines if the user has access to server specific pages. If set to false, which is the default, the user will not have access to the Databases, Process list and Variables pages, as well as the server-related Query, Import and Export pages.
The corresponding menu entries will not be displayed in the sidebar menu.
The databases and schemas options restrict the user access to the listed databases and schemas.
The query audit
All the queries executed by the users can be saved in a database and viewed in a dedicated page.
Creating the query audit database
SQL scripts are provided in the https://github.com/lagdo/jaxon-dbadmin/tree/main/migrations repo to create the query audit database on PostgreSQL, MySQL (or MariaDB), or SQLite.
For each DBMS, the script is in the 01-create-command-tables.up.sql file in the corresponding subdir.
Writing in the query audit
The query audit writer options are located in the audit section in the config/dbadmin.php config file.
'audit' => [ 'options' => [ 'enduser' => [ 'enabled' => true, ], 'history' => [ 'enabled' => true, 'distinct' => true, 'limit' => 10, ], ], 'database' => [ // Same as the "servers" items, but "name" is the database name. 'driver' => 'pgsql', 'host' => "env(LOGGING_DB_HOST)", 'port' => "env(LOGGING_DB_PORT)", 'username' => "env(LOGGING_DB_USERNAME)", 'password' => "env(LOGGING_DB_PASSWORD)", 'name' => 'auditdb', ], ],
The audit.database section contains the audit database connection options.
The options are the same as in the above database servers options, excepted that the name option is the database name.
The audit.options.enduser.enabled option enables the audit, for queries executed in the query builder and the query editor.
The audit.options.history.enabled option enables the audit for queries executed in the editor, and the display of the query history in the query editor page.
When the query history is enabled, the audit.options.history.distinct option enables the removal of duplicates in the listed queries, while the audit.options.history.limit option sets the max number of queries for pagination.
Viewing the query audit
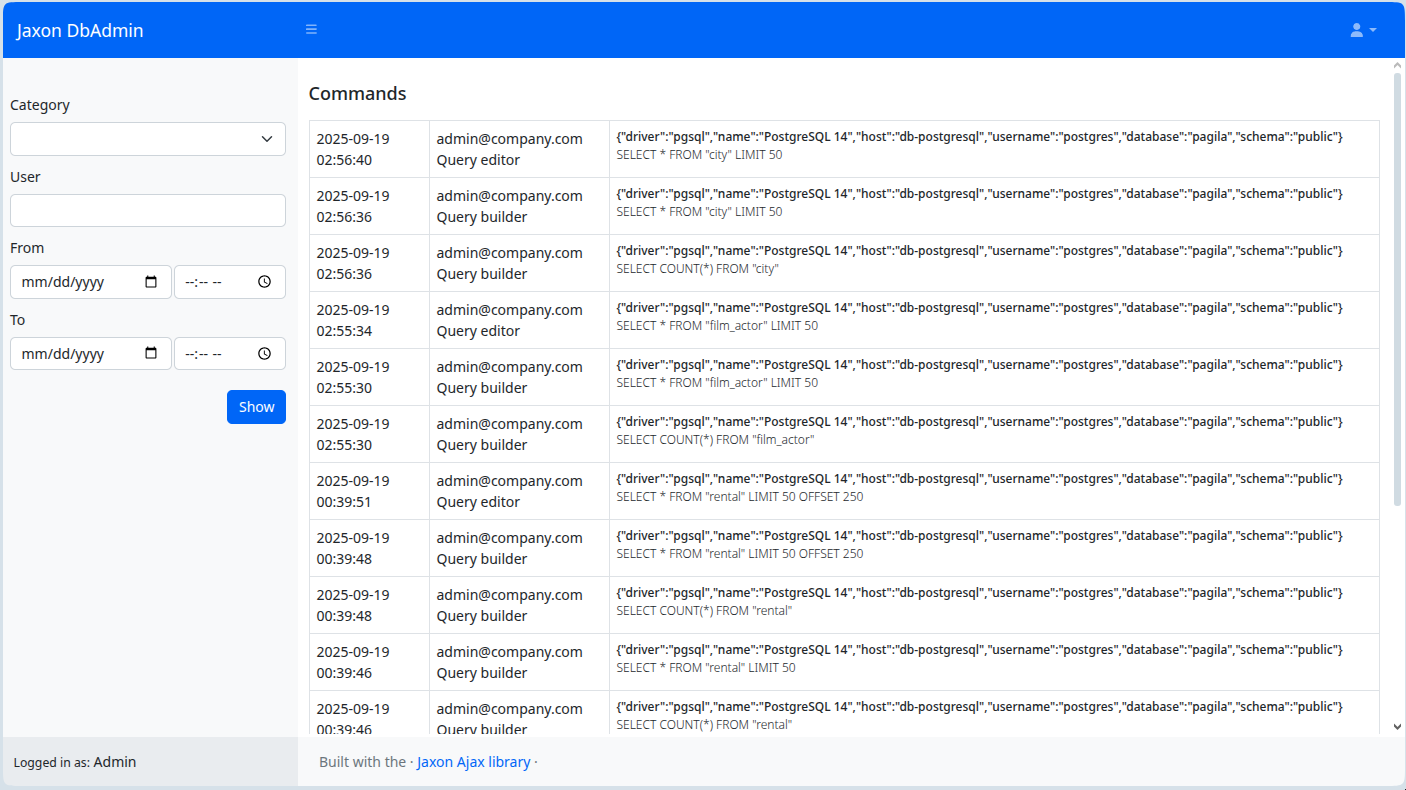
The Audit logs entry in the top right menu (and the /audit link) gives access to a page which displays the logged queries.
The form in the sidebar provides fields to filter the queries based on various criteria.
The database connection options are the same that are used to write the audit logs, as described in the above section.
'audit' => [ 'database' => [ // Same as the "servers" items, but "name" is the database name. 'driver' => 'pgsql', 'host' => "env(LOGGING_DB_HOST)", 'port' => "env(LOGGING_DB_PORT)", 'username' => "env(LOGGING_DB_USERNAME)", 'password' => "env(LOGGING_DB_PASSWORD)", 'name' => 'auditdb', ], 'allowed' => [ // The emails of users that are allowed to access the audit page. 'admin@company.com', ], ],
The access to that page is limited to the user accounts with the email listed in the audit.allowed option in the config/dbadmin.php file.
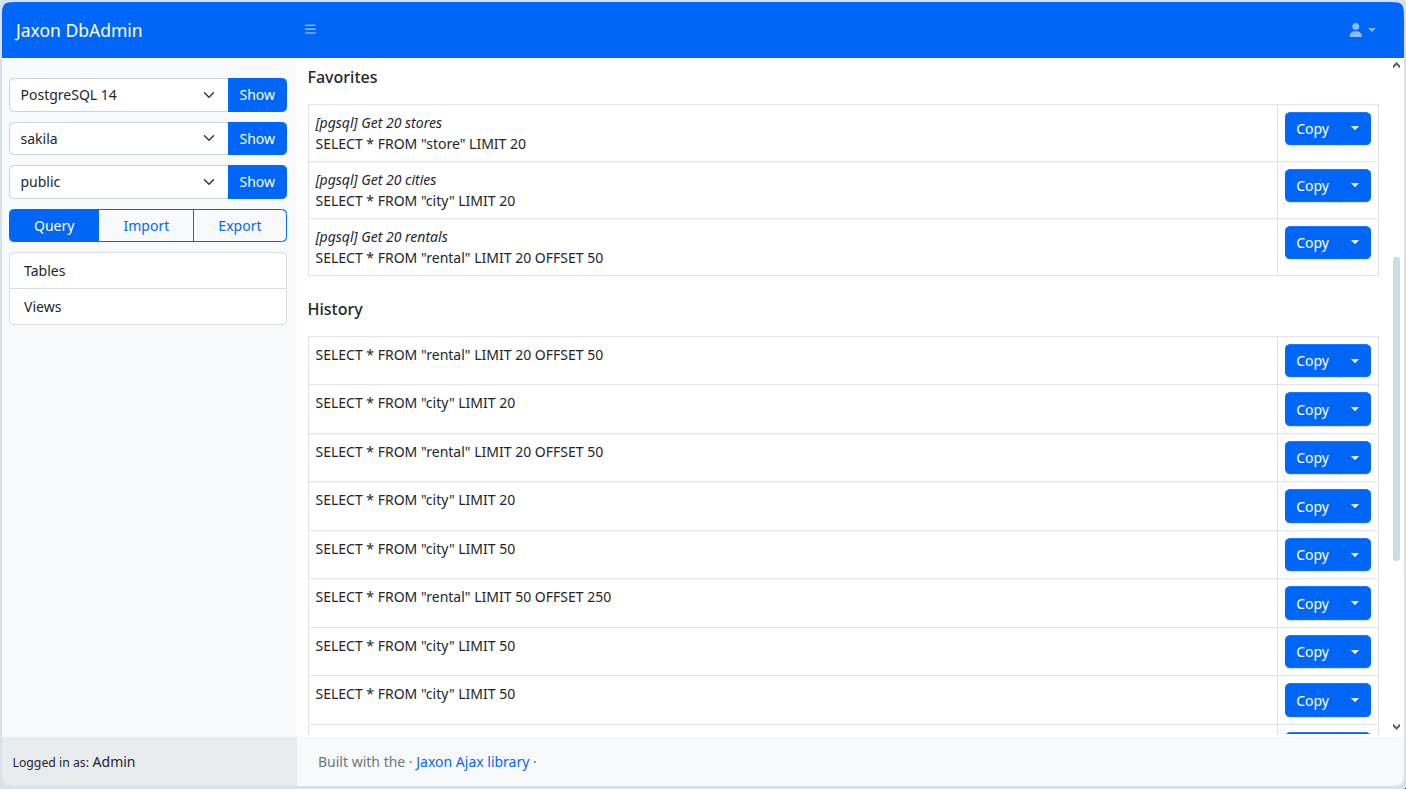
The query history and favorites
The queries saved in the logs from the query editor are displayed in the user query history, when the corresponding option is enabled.
Additionally, the user can also save his preferred queries in the audit database, using the Save button in the query edition page.
Both the history and favorites queries are displayed in the query page. From those two tables, the user can copy or insert the query code in the editor.
The queries in the favorites can also be modified or deleted.
Data export
Databases can be exported to various types of files: SQL, CSV, and more.
The export feature is configured with two callbacks.
The writer callback saves the export data content in a file. It takes the content and the file name as parameters, and returns the URI to the exported file.
It must return an empty string in case of error, and the web app must be configured to return the file content on a request to the URI.
The reader callback takes an export file name as parameter, then reads and returns its content.
Both callbacks can use the Jaxon Storage, as in the example below, to read and write the exported files, which can then be saved on different types of filesystems, thanks to the Flysystem library.
The callbacks can also save the files in different locations, depending for example on the application user.
In this example, each user files will be store in the /path/to/exports<user-email-slug>/ dir.
A user will not be able to get access to another user files from his account.
use Illuminate\Support\Str; use Jaxon\Storage\StorageManager; use League\Flysystem\FilesystemException; use League\Flysystem\UnableToReadFile; use League\Flysystem\UnableToWriteFile; use function Jaxon\jaxon; function getExportPath(string $filename): string { return Str::slug(auth()->user()->email) . "/$filename"; } return [ 'app' => [ 'storage' => [ 'stores' => [ 'exports' => [ 'adapter' => 'local', 'dir' => "/path/to/exports", ], ], ], 'packages' => [ Lagdo\DbAdmin\Db\DbAdminPackage::class => [ 'servers' => [ // The database servers ], 'export' => [ 'writer' => function(string $content, string $filename): string { try { // Make a Filesystem object with the storage.exports options. $storage = jaxon()->di()->g(StorageManager::class)->get('exports'); $storage->write(getExportPath($filename), "$content\n"); } catch (FilesystemException|UnableToWriteFile) { return ''; } // Return the link to the exported file. return "/export.php?file=$filename"; }, 'reader' => function(string $filename): string { try { // Make a Filesystem object with the storage.exports options. $storage = jaxon()->di()->g(StorageManager::class)->get('exports'); $filepath = getExportPath($filename); return !$storage->fileExists($filepath) ? "No file $filename found." : $storage->read($filepath); } catch (FilesystemException|UnableToReadFile) { return "No file $filename found."; } }, ], ], ], ], ... ];
Data import (with file upload)
SQL files can be uploaded and executed on a server. This feature is implemented using the Jaxon ajax upload and Jaxon Storage packages, which then needs to be configured in the Jaxon config file.
'app' => [ 'storage' => [ 'stores' => [ 'uploads' => [ 'adapter' => 'local', 'dir' => '/path/to/the/upload/dir', ], ], ], 'upload' => [ 'enabled' => true, 'files' => [ 'sql_files' => [ 'storage' => 'uploads', ], ], ], ],
In this example, sql_files is the name attribute of the file upload field, and of course /path/to/the/upload/dir needs to be writable.
Other parameters can also be defined to limit the size of the uploaded files or retrict their extensions or mime types.
the Jaxon ajax upload documentation
Contributing
If you're interested in helping improve this project, contributions are very welcome:
- Bug reports: If something doesn't work as expected
- Feature suggestions: Ideas for improvements
- Code contributions: Help fix issues or add features
- Documentation: Help make things clearer for others
- Testing: Help identify problems
Feel free to open issues or pull requests. Even small improvements are appreciated.
Technical Details
- Backend: Laravel (PHP), Jaxon
- Frontend: Bootstrap, Blade, UI Builder
- Containerization: Docker support included
The Jaxon DbAdmin application is actually the integration of the Jaxon DbAdmin package, which is an extension of the Jaxon library, with the Laravel framework, using the Laravel integration extension.
The UI is built with the HTML UI Builder package, and generated with the Bootstrap 5 HTML UI Builder adapter package.
The database access code (and thus the provided features) originates from Adminer. The original code was separated into multiple Composer packages, and refactored to take advantage of advanced PHP features: namespaces, interfaces, dependency injection, and so on.
License
BSD 3-Clause License - feel free to use, modify, and distribute.