sourcepot / datapool
The Datapool PHP framework
Requires
- php: ^8.0
- directorytree/imapengine: ^v1.15.5
- guzzlehttp/guzzle: ^7.0
- hfig/mapi: >=v1.4.2
- horstoeko/zugferd: ^1
- michelf/php-markdown: ^2.0.0
- monolog/monolog: ^3.5.0
- phpmailer/phpmailer: ^6.10.0
- phpoffice/phpspreadsheet: >=2.2.1
- psr/log: ^3
- smalot/pdfparser: ^v2.7.0
- sourcepot/asset: ^v2.3.0
- sourcepot/bankholidays: ^v2.2.0
- sourcepot/checkentries: ^v1.5.0
- sourcepot/match: ^v1.6.4
- sourcepot/mediaplayer: ^v4.3.1
- sourcepot/ops: ^v1.3.0
- sourcepot/sms: ^v2.4.3
- sourcepot/statistic: ^v1.1.0
- spatie/pdf-to-text: ^1.52.0
- dev-main
- v4.35.0
- v4.34.0
- v4.33.0
- v4.32.0
- v4.31.1
- v4.31.0
- v4.30.0
- v4.29.1
- v4.29.0
- v4.28.0
- v4.27.3
- v4.27.2
- v4.27.1
- v4.27.0
- v4.26.3
- v4.26.2
- v4.26.1
- v4.26.0
- v4.25.3
- v4.25.2
- v4.25.1
- v4.25.0
- v4.24.7
- v4.24.6
- v4.24.5
- v4.24.4
- v4.24.3
- v4.24.2
- v4.24.1
- v4.24.0
- v4.23.3
- v4.23.2
- v4.23.1
- v4.23.0
- v4.22.0
- v4.21.0
- v4.20.1
- v4.20.0
- v4.19.0
- v4.18.1
- v4.18.0
- v4.17.7
- v4.17.6
- v4.17.5
- v4.17.4
- v4.17.3
- v4.17.2
- v4.17.1
- v4.17.0
- v4.16.6
- v4.16.5
- v4.16.4
- v4.16.3
- v4.16.2
- v4.16.1
- v4.16.0
- v4.15.2
- v4.15.1
- v4.15.0
- v4.14.0
- v4.13.1
- v4.13.0
- v4.12.6
- v4.12.5
- v4.12.4
- v4.12.3
- v4.12.2
- v4.12.1
- v4.12.0
- v4.11.0
- v4.10.1
- v4.10.0
- v4.9.5
- v4.9.4
- v4.9.3
- v4.9.2
- v4.9.1
- v4.9.0
- v4.8.2
- v4.8.1
- v4.8.0
- v4.7.0
- v4.6.2
- v4.6.1
- v4.6.0
- v4.5.0
- v4.4.1
- v4.4.0
- v4.3.0
- v4.2.1
- v4.2.0
- v4.1.1
- v4.1.0
- v4.0.4
- v4.0.3
- v4.0.2
- v4.0.1
- v4.0.0
- v3.1.1
- v3.1.0
- v3.0.2
- v3.0.1
- v3.0.0
- v2.6.12
- v2.6.11
- v2.6.10
- v2.6.9
- v2.6.8
- v2.6.7
- v2.6.6
- v2.6.5
- v2.6.4
- v2.6.3
- v2.6.2
- v2.6.1
- v2.6.0
- v2.5.4
- v2.5.3
- v2.5.2
- v2.5.1
- v2.5.0
- v2.4.0
- v2.3.0
- v2.2.0
- v2.1.8
- v2.1.7
- v2.1.6
- v2.1.5
- v2.1.4
- v2.1.3
- v2.1.2
- v2.1.1
- v2.1.0
- v2.0.0
- v1.5.5
- v1.5.4
- v1.5.3
- v1.5.2
- v1.5.1
- v1.5.0
- v1.4.12
- v1.4.11
- v1.4.10
- v1.4.9
- v1.4.8
- v1.4.7
- v1.4.6
- v1.4.5
- v1.4.4
- v1.4.3
- v1.4.2
- v1.4.1
- v1.4.0
- v1.3.4
- v1.3.3
- v1.3.2
- v1.3.1
- v1.3.0
- v1.2.4
- v1.2.3
- v1.2.2
- v1.2.1
- v1.2.0
- v1.1.6
- v1.1.5
- v1.1.4
- v1.1.3
- v1.1.2
- v1.1.1
- v1.1.0
- v1.0.9
- v1.0.8
- v1.0.7
- v1.0.6
- v1.0.5
- v1.0.4
- v1.0.3
- v1.0.2
- v1.0.1
- v1.0.0
- v0.4.8
- v0.4.7
- v0.4.6
- v0.4.5
- v0.4.4
- v0.4.3
- v0.4.2
- v0.4.1
- v0.3.10
- v0.3.9
- v0.3.8
- v0.3.7
- v0.3.6
- v0.3.5
- v0.3.4
- v0.3.3
- v0.3.2
- v0.3.1
- v0.2.20
- v0.2.19
- v0.2.18
- v0.2.17
- v0.2.16
- v0.2.15
- v0.2.14
- v0.2.13
- v0.2.12
- v0.2.11
- v0.2.10
- v0.2.9
- v0.2.8
- v0.2.7
- v0.2.6
- v0.2.5
- v0.2.4
- v0.2.3
- v0.2.2
- v0.2.1
- v0.1.20
- v0.1.19
- v0.1.18
- v0.1.17
- v0.1.16
- v0.1.15
- v0.1.14
- v0.1.13
- v0.1.12
- v0.1.11
- v0.1.10
- v0.1.9
- v0.1.8
- v0.1.7
- v0.1.6
- v0.1.5
- v0.1.4
- v0.1.3
- v0.1.2
- v0.1.1
- v0.1.0
- dev-dev
This package is auto-updated.
Last update: 2026-03-08 18:10:51 UTC
README
Datapool is a versatile modular web application.
Advantages of a web application in contrast to a desktop application
- Runs on a wide range of devices, the web browser is the runtime environment
- The user interface is always up-to-date thanks to the use of HTML as the living standard (less use of JavaScript) and modern web browsers
- Simple interaction with other web services
- Established infrastructures available for data backup
Basic features
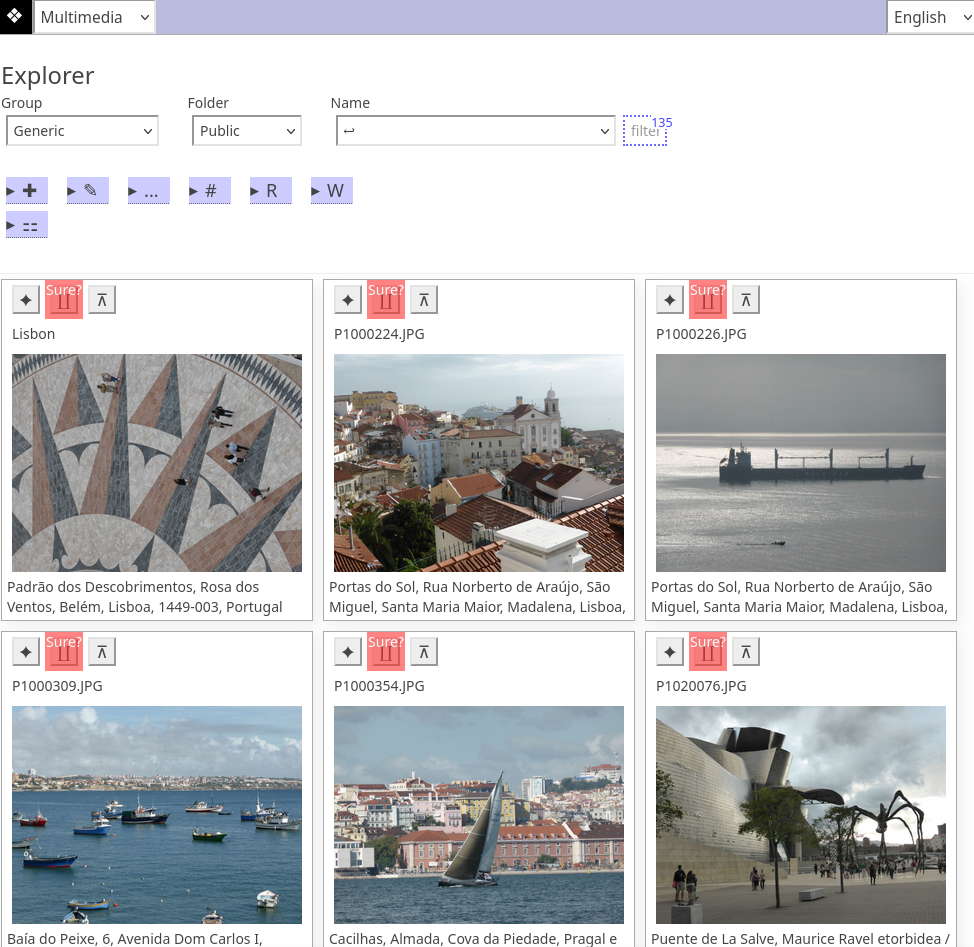
- Media-/File-Explorer: structured data and file storage based on selectors Group, Folder, Name, EntryId
- DataExplorer: process driven dataflow and dataprocessing
- MediaPlayer: creating and playing video playlists, see https://github.com/SourcePot/mediaplayer
- Calendar: calendar sheet holding single and recurring events which can be connected to the DataExplorer
- Forum and Chat: communication platform for the web application users
- Flexible RSS feed reader
- Remote client interface: connecting remote sensor platforms, see https://github.com/SourcePot/PIclient
- Role-based access control to apps and data: 16 user roles, e.g. web admin, config admin, member, registered, public etc.
- Interfaces: for adding your apps, receivers, transmitters (e.g. https://github.com/SourcePot/sms), processors etc.
- Comprehensive logger
Use cases
The two typical use cases are process-driven data processing and a content management system. The functionality of complex spreadsheets can alternatively be easily implemented as a process data flow. Easily accessible intermediate results help to maintain an overview and to find and fix problems.
Process-driven data processing - DataExplorer
- Data sources can be media-files, pdf-documents, spreadsheet-files either uploaded manually or downloaded from an email inbox
- External devices can provide data or files through a client interface
- The result of the processing can be spreadsheet-files, zip-files, emails or SMS-messages
- Data processing can be controlled manually or by trigger derived from values or calendar events
- Processes can be easily designed and adopted via a graphical user interface
- Processes can easily be exported or imported to other systems running Datapool
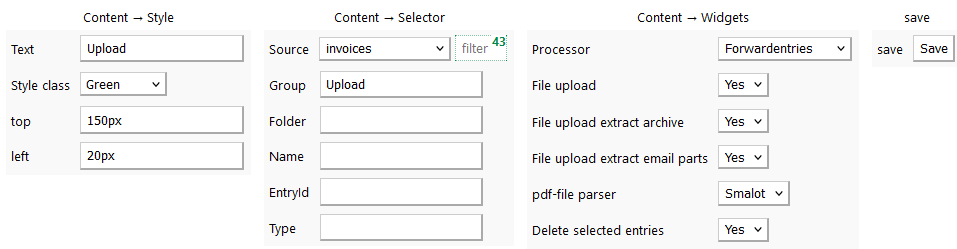
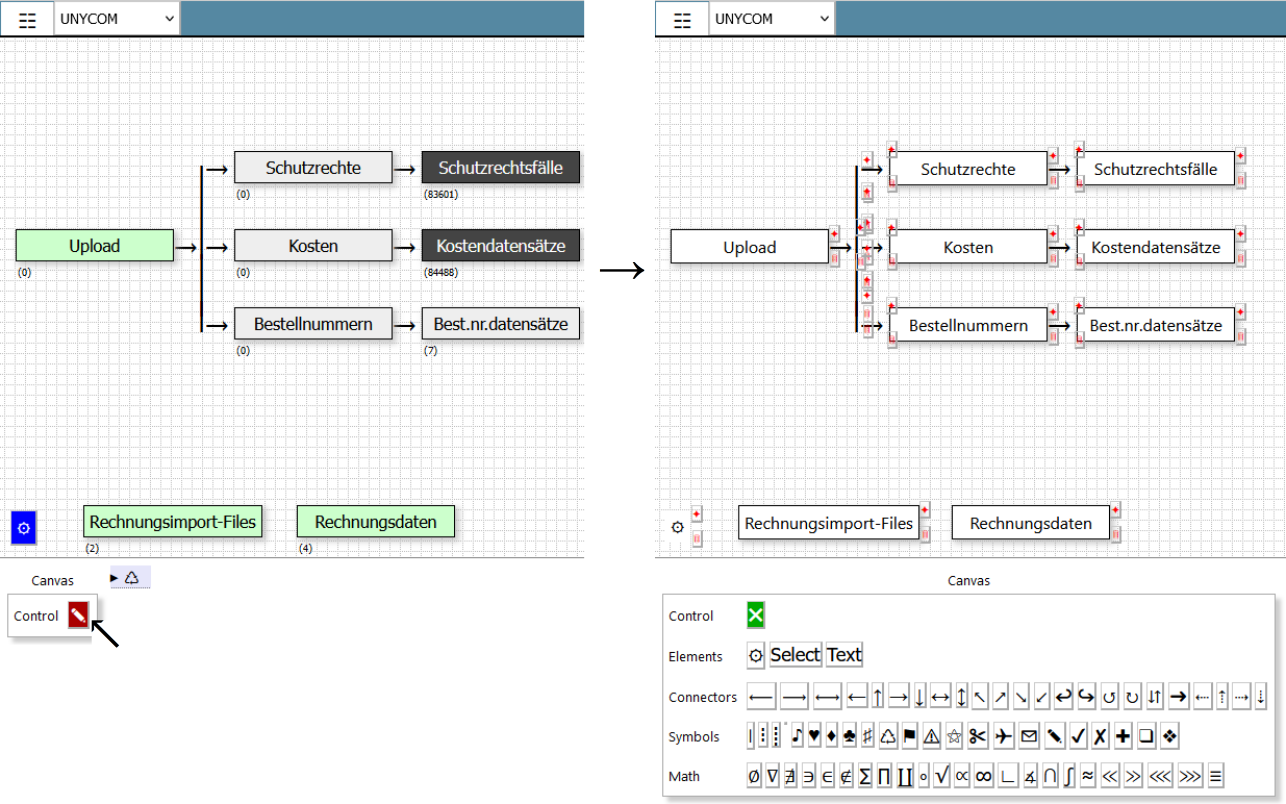
Data apps use the DataExplorer class SourcePot\Datapool\Foundation\DataExplorer. The data explorer provides a blank canvas to create data crunching processes graphically. This is done by adding canvas elements and by configuring their properties. A canvas element is a view of a database table. The database table view applies a selector Content → Selector (see the figure below). Features can be added to the canvas element such as File upload (e.g. for invoice documents, email etc.), pdf-parser and/or a processor. There is a set of basic processors to e.g. match, map or forward entries. There are also a basic processors to create pdf-documents, to send emails or SMS.
The DataExplorer has two modes: view and edit The figure below shows how to togle between view and edit mode. In edit mode each canvas element can be dragged, selected or deleted. To change canvas element properties the canvas element needs to be selected by clicking on the diamond shaped red button of the respective canvas element.
Content management
In general all data and files are stored as entries. An entry consists of a databease table entry and, in some cases, of a linked file stored in a designated filespace on the server.
The database table entries contain of the following fields (cells);
- Selector fields: EntryId, Group, Folder, Type and Name,
- A content data field: Content,
- A meta data field: Params,
- Access control fields: Owner, Write, Read, Privileges and
- Various control data fields: Date, Expires, etc.
Multiple entries are presented either as tiles or a table (with one ro per entry). The presentation of a selected entry can be configured as required.
Get Started
You need to host the web application through a web server or local host (e.g. your personal computer). The server can be set up on a wide range of systems such as Linux, UNIX, MS Windows.
Requirements
This software is designed to run on a web server, i.e. the user interface is the web browser.
The web application requires:
- a server software (e.g. Apache, nginx installed on a web server or local computer),
- PHP 8+ and
- a database (and a database user, which will be used by the web application).
To run Datapool on your computer as local host, you could install XAMPP Apache + MariaDB + PHP + Perl (see https://www.apachefriends.org/). The following example uses XAMPP as the software environment.This works well as local host on a MS Windows computer or Linux system (e.g. Debian).
Personally, I use Composer to install the web application with all its dependencies and the folder structure. If you like to use Composer you will need to install the software on your computer or server, see https://getcomposer.org/download/ for details.
I tend to install the web application on my personal computer first. This serves as my local backup and can be used for final tests. In a later step, I copy the whole Datapool directory, with the exception of the ../src/setup/ and ../src/filespace/ directories, with all it's files to the web server using FTP (FileZilla).
Installing the web application
- Choose your target directory on your web server or your computer and run Composer
composer create-project sourcepot/datapool {add your target directory here}. This will create, among other things, the../src/www/-subdirectory, which is the www-root and should be accessible through the network, i.e. by a client web browser. If you use XAMPP, locate the XAMPP directory, e.g..../xampp/htdocs/. Your web applications' directories and files should be located there after successfully running Composer with this target directory. - Create a database and a corresponding database user. Set the database collation to utf8mb4_unicode_ci.
Note
It may be that PHP extensions are missing on your system, for example. Composer will exit the script with an exception and tell you the name of the missing extension.
Example code: adding missing extensions on the local host
This is based on a Debian 12 (bookworm) 64-bit system with a XAMPP installation.
sudo apt-get install php-xml
sudo apt-get install php-gd
sudo apt-get install php-zip
sudo apt-get install php-bcmath
sudo apt-get install php-curl
Connecting the web application with the database
- Call the webpage through a web browser. This will create an error message since the database access needs to be set up. You can check the error logs which are located in the
../src/debugging/-subdirectory. Each error generates a JSON-file containing the error details. - Calling the webpage creates the file
../src/setup/Database/connect.jsonwhich contains the database user credentials. Use a text editor to update or match the credentials with the database user credentials. - If the database as well as the database user are set up correctly, and the user credentials used by Datapool match the database user, the web application should (when reloaded) show an empty web page with a menu bar at the top and the logger at the bottom of the web browser.
Create your Admin account for your web application
- Refresh the webpage. This will create an initial admin user account.
- Use the Login page to register your own new account.
- Use the initial admin account to login and change your newly registered own account. Change your own account priviledges from
registeredtoadminaccess level (Admin → Account). The initial admin credentials can be found in the../src/setup/User/initAdminAccount.jsondirectory. - Delete the initial admin user account.
- Update the webmaster email address Admin → Admin → Page settings → EmailWebmaster. Allways use the ✓ button to save changes.
Important
Remember to ensure security, you need to adjust all file permissions to the minimum necessary access level. Especially if you run the application on a publicly accessible server. Make sure that only the ../src/www/-subdirectory is visible to the public and public write-access must be prohibited.
Initial adjustments
After you have set up your admin account you should login and update the webmaster email address Admin → Admin → Page settings → EmailWebmaster. Allways use the ✓ button to save changes.
Dependencies: PEAR
PEAR may be required for processing office documents such as emails. If the upload of emails fails, the php script might have failed to include PEAR. The exception "Failed opening required 'PEAR.php' (include_path='/var/www/vhosts/... indicates a faulty dicetory setting for PEAR. Check if PEAR is installed and the location of the PEAR directory is set correctly on the server. If PEAR is installed, you can check the directory as follows:
If PEAR is not currently installed, it can be installed on a Linux system using the following command:
sudo apt-get install php-pear
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
The following command returns the PEAR directory:
pear config-get php_dir
> /usr/share/php
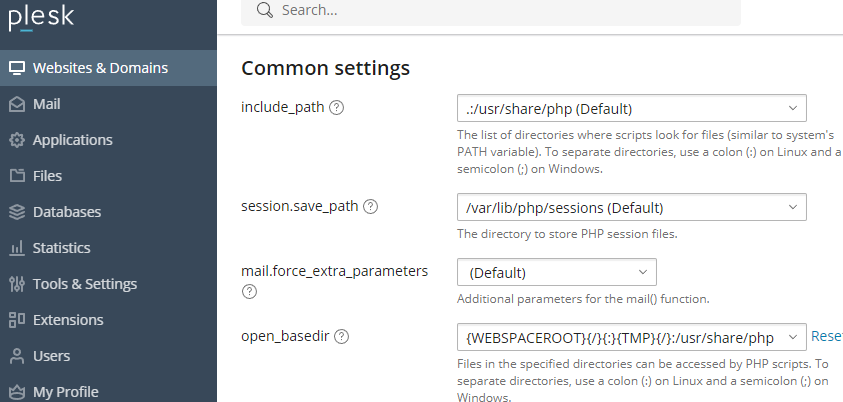
If you use PLESK for your server administration, you can add the correct path as follows in Websites & Domains, PHP Settings for...:
You need to append the PEAR folder path relative to the selected PHP version to include_path e.g.
.:/opt/plesk/php/8.4/share/pear
and open_basedir e.g.
{WEBSPACEROOT}{/}{:}{TMP}{/}:/opt/plesk/php/8.4/share/pear
Under the Hood
Datapool is based on an object collection oc, i.e. a collection of objects instantiated from the PHP-classes of the ../php/ folder. The object collection is created by the constructor of class ../php/Root.php each time the web application is called by a client e.g. web browser.
../php/Root.php provides the collection to all instantiated classes which implement the method loadOc(array $oc). Typically the classes have a private property oc which is set/updated by the loadOc method of the class.
The configuration file ../setup/objectList.csv determines the order of creation of the objects. With the private property registerVendorClasses of class ../php/Root.php vendor classes can be added to the object collection. Otherwise, an instance of a vendor class can (as usual) be created within the source code when required.
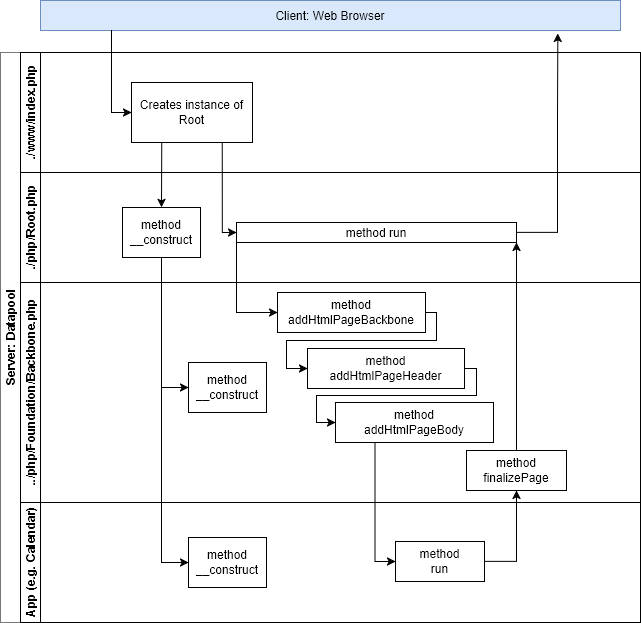
Web page creation
The following flowchart shows the sequence of object instantiations, method calls and content creation.
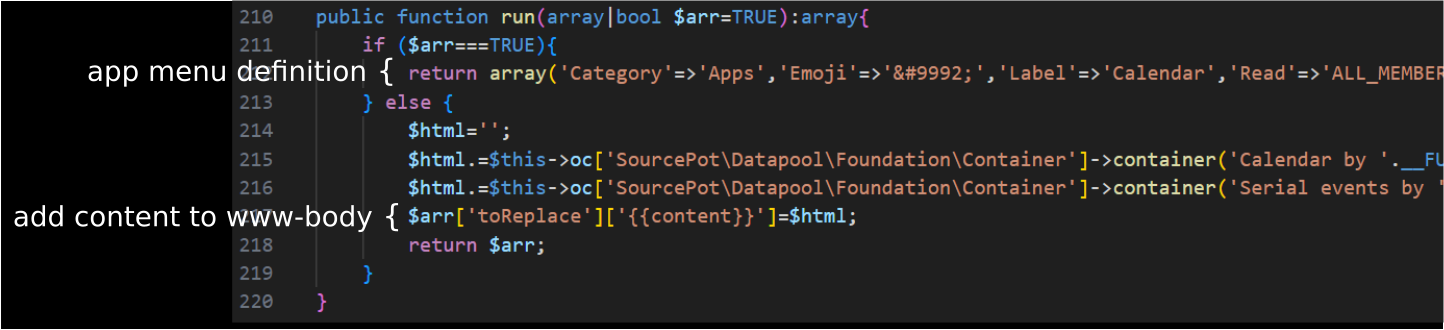
Any class which implements the SourcePot\Datapool\Interfaces\App interface must provide a run method. The run method defines the app specific menu item, the app visibility and the method adds the app specific web page content. The following figure shows the run method of the calendar app SourcePot\Datapool\GenericApps\Calendar→run().